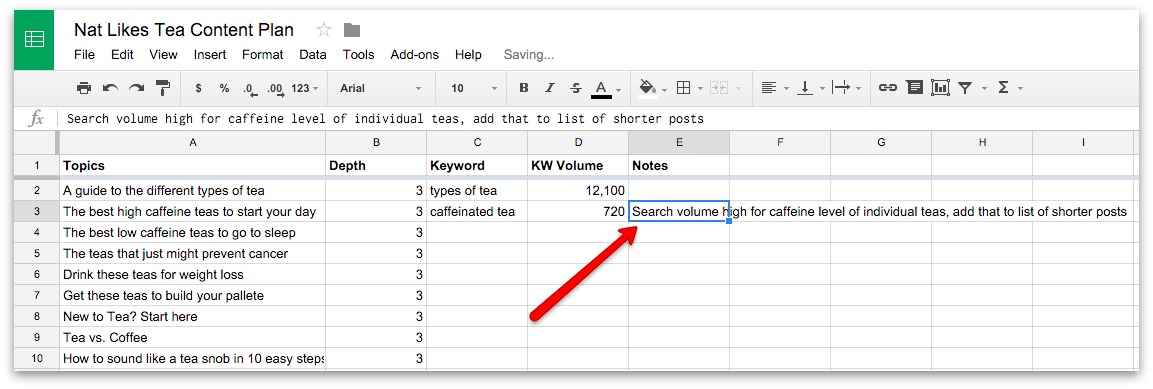
Cogs and Calculators
It is a measure of the brilliance of the abacus, invented in the Middle East circa 500 BC, that it remained the fastest form of calculator until the middle of the 17th century. Then, in 1642, aged only 18, French scientist and philosopher
Blaise Pascal (1623–1666) invented the first practical mechanical
calculator, the Pascaline, to help his tax-collector father do his sums. The machine had a series of interlocking cogs (
gear wheels with teeth around their outer edges) that could add and subtract decimal numbers. Several decades later, in 1671, German mathematician and philosopher
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646–1716) came up with a similar but more advanced machine. Instead of using cogs, it had a "stepped drum" (a cylinder with teeth of increasing length around its edge), an innovation that survived in mechanical calculators for 300 hundred years. The Leibniz machine could do much more than Pascal's: as well as adding and subtracting, it could multiply, divide, and work out square roots. Another pioneering feature was the first
memory store or "register."
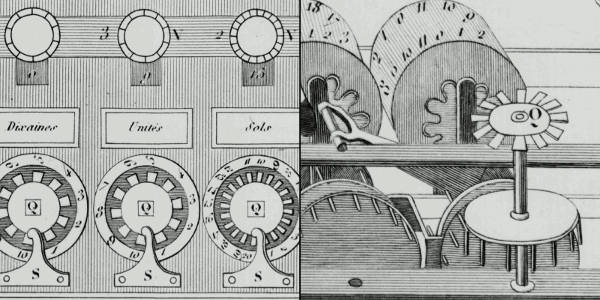
Artwork: Pascaline: Two details of Blaise Pascal's 17th-century calculator. Left: The "user interface": the part where you dial in numbers you want to calculate. Right: The internal gear mechanism. Picture courtesy of US Library of Congress.
Apart from developing one of the world's earliest mechanical calculators, Leibniz is remembered for another important contribution to computing: he was the man who invented binary code, a way of representing any decimal number using only the two digits zero and one. Although Leibniz made no use of binary in his own calculator, it set others thinking. In 1854, a little over a century after Leibniz had died, Englishman
George Boole (1815–1864) used the idea to invent a new branch of mathematics called Boolean algebra. In modern computers, binary code and Boolean algebra allow computers to make simple decisions by comparing long strings of zeros and ones. But, in the 19th century, these ideas were still far ahead of their time. It would take another 50–100 years for mathematicians and computer scientists to figure out how to use them (find out more in our articles about
calculators and
logic gates).
Engines of Calculation
Neither the abacus, nor the mechanical calculators constructed by Pascal and Leibniz really qualified as computers. A calculator is a device that makes it quicker and easier for people to do sums—but it needs a human operator. A computer, on the other hand, is a machine that can operate automatically, without any human help, by following a series of stored instructions called a program (a kind of mathematical recipe). Calculators evolved into computers when people devised ways of making entirely automatic, programmable calculators.
Photo: Punched cards: Herman Hollerith perfected the way of using punched cards and paper tape to store information and feed it into a machine. Here's a drawing from his 1889 patent Art of Compiling Statistics (US Patent#395,782), showing how a strip of paper (yellow) is punched with different patterns of holes (orange) that correspond to statistics gathered about people in the US census. Picture courtesy of US Patent and Trademark Office.
The first person to attempt this was a rather obsessive, notoriously grumpy English mathematician named
Charles Babbage(1791–1871). Many regard Babbage as the "father of the computer" because his machines had an input (a way of feeding in numbers), a memory (something to store these numbers while complex calculations were taking place), a processor (the number-cruncher that carried out the calculations), and an output (a printing mechanism)—the same basic components shared by all modern computers. During his lifetime, Babbage never completed a single one of the hugely ambitious machines that he tried to build. That was no surprise. Each of his programmable "engines" was designed to use tens of thousands of precision-made gears. It was like a pocket watch scaled up to the size of a
steam engine, a Pascal or Leibniz machine magnified a thousand-fold in dimensions, ambition, and complexity. For a time, the British government financed Babbage—to the tune of £17,000, then an enormous sum. But when Babbage pressed the government for more money to build an even more advanced machine, they lost patience and pulled out. Babbage was more fortunate in receiving help from
Augusta Ada Byron (1815–1852), Countess of Lovelace, daughter of the poet Lord Byron. An enthusiastic mathematician, she helped to refine Babbage's ideas for making his machine programmable—and this is why she is still, sometimes, referred to as the world's first computer programmer. Little of Babbage's work survived after his death. But when, by chance, his notebooks were rediscovered in the 1930s, computer scientists finally appreciated the brilliance of his ideas. Unfortunately, by then, most of these ideas had already been reinvented by others.
Babbage had intended that his machine would take the drudgery out of repetitive calculations. Originally, he imagined it would be used by the army to compile the tables that helped their gunners to fire cannons more accurately. Toward the end of the 19th century, other inventors were more successful in their effort to construct "engines" of calculation. American statistician Herman Hollerith (1860–1929) built one of the world's first practical calculating machines, which he called a tabulator, to help compile census data. Then, as now, a census was taken each decade but, by the 1880s, the population of the United States had grown so much through immigration that a full-scale analysis of the data by hand was taking seven and a half years. The statisticians soon figured out that, if trends continued, they would run out of time to compile one census before the next one fell due. Fortunately, Hollerith's tabulator was an amazing success: it tallied the entire census in only six weeks and completed the full analysis in just two and a half years. Soon afterward, Hollerith realized his machine had other applications, so he set up the Tabulating Machine Company in 1896 to manufacture it commercially. A few years later, it changed its name to the Computing-Tabulating-Recording (C-T-R) company and then, in 1924, acquired its present name: International Business Machines (IBM).
Bush and the bomb
The history of computing remembers colorful characters like Babbage, but others who played important—if supporting—roles are less well known. At the time when C-T-R was becoming IBM, the world's most powerful calculators were being developed by US government scientist
Vannevar Bush (1890–1974). In 1925, Bush made the first of a series of unwieldy contraptions with equally cumbersome names: the New Recording Product Integraph Multiplier. Later, he built a machine called the Differential Analyzer, which used gears, belts, levers, and shafts to represent numbers and carry out calculations in a very physical way, like a gigantic mechanical slide rule. Bush's ultimate calculator was an improved machine named the Rockefeller Differential Analyzer, assembled in 1935 from 320 km (200 miles) of wire and 150
electric motors. Machines like these were known as
analog calculators—analog because they stored numbers in a physical form (as so many turns on a wheel or twists of a belt) rather than as digits. Although they could carry out incredibly complex calculations, it took several days of wheel cranking and belt turning before the results finally emerged.

Photo: A Differential Analyzer. The black part in the background is the main part of the machine. The operator sits at a smaller console in the foreground. Picture courtesy of NASA on the Commons (where you can download a larger version of this photo).
Impressive machines like the Differential Analyzer were only one of several outstanding contributions Bush made to 20th-century technology. Another came as the teacher of
Claude Shannon (1916–2001), a brilliant mathematician who figured out how electrical circuits could be linked together to process binary code with Boolean algebra (a way of comparing binary numbers using logic) and thus make simple decisions. During World War II, President Franklin D. Roosevelt appointed Bush chairman first of the US National Defense Research Committee and then director of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD). In this capacity, he was in charge of the Manhattan Project, the secret $2-billion initiative that led to the creation of the atomic bomb. One of Bush's final wartime contributions was to sketch out, in 1945, an idea for a memory-storing and sharing device called Memex that would later inspire Tim Berners-Lee to invent the
World Wide Web. Few outside the world of computing remember Vannevar Bush today—but what a legacy! As a father of the digital computer, an overseer of the atom bomb, and an inspiration for the Web, Bush played a pivotal role in three of the 20th-century's most far-reaching technologies.
Turing—tested
Many of the pioneers of computing were hands-on experimenters—but by no means all of them. One of the key figures in the history of 20th-century computing, Alan Turing(1912–1954) was a brilliant Cambridge mathematician whose major contributions were to the theory of how computers processed information. In 1936, at the age of just 23, Turing wrote a groundbreaking mathematical paper called "On computable numbers, with an application to the Entscheidungsproblem," in which he described a theoretical computer now known as a Turing machine (a simple information processor that works through a series of instructions, reading data, writing results, and then moving on to the next instruction). Turing's ideas were hugely influential in the years that followed and many people regard him as the father of modern computing—the 20th-century's equivalent of Babbage.
Although essentially a theoretician, Turing did get involved with real, practical machinery, unlike many mathematicians of his time. During World War II, he played a pivotal role in the development of code-breaking machinery that, itself, played a key part in Britain's wartime victory; later, he played a lesser role in the creation of several large-scale experimental computers including ACE (Automatic Computing Engine), Colossus, and the Manchester/Ferranti Mark I (described below). Today, Alan Turing is best known for conceiving what's become known as the Turing test, a simple way to find out whether a computer can be considered intelligent by seeing whether it can sustain a plausible conversation with a real human being.
The first modern computers
The World War II years were a crucial period in the history of computing, when powerful gargantuan computers began to appear. Just before the outbreak of the war, in 1938, German engineer Konrad Zuse (1910–1995) constructed his Z1, the world's first programmable binary computer, in his parents' living room. The following year, American physicist John Atanasoff (1903–1995) and his assistant, electrical engineer Clifford Berry (1918–1963), built a more elaborate binary machine that they named the Atanasoff Berry Computer (ABC). It was a great advance—1000 times more accurate than Bush's Differential Analyzer. These were the first machines that used electrical switches to store numbers: when a switch was "off", it stored the number zero; flipped over to its other, "on", position, it stored the number one. Hundreds or thousands of switches could thus store a great many binary digits (although binary is much less efficient in this respect than decimal, since it takes up to eight binary digits to store a three-digit decimal number). These machines were digital computers: unlike analog machines, which stored numbers using the positions of wheels and rods, they stored numbers as digits.
The first large-scale digital computer of this kind appeared in 1944 at Harvard University, built by mathematician
Howard Aiken (1900–1973). Sponsored by IBM, it was variously known as the Harvard Mark I or the IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator (ASCC). A giant of a machine, stretching 15m (50ft) in length, it was like a huge mechanical calculator built into a wall. It must have
sounded impressive, because it stored and processed numbers using "clickety-clack" electromagnetic
relays (electrically operated
magnets that automatically switched lines in
telephone exchanges)—no fewer than 3304 of them. Impressive they may have been, but relays suffered from several problems: they were large (that's why the Harvard Mark I had to be so big); they needed quite hefty pulses of power to make them switch; and they were slow (it took time for a relay to flip from "off" to "on" or from 0 to 1).

Photo: An analog computer being used in military research in 1949. Picture courtesy of NASA on the Commons(where you can download a larger version.
Most of the machines developed around this time were intended for military purposes. Like Babbage's never-built mechanical engines, they were designed to calculate artillery firing tables and chew through the other complex chores that were then the lot of military mathematicians. During World War II, the military co-opted thousands of the best scientific minds: recognizing that science would win the war, Vannevar Bush's Office of Scientific Research and Development employed 10,000 scientists from the United States alone. Things were very different in Germany. When Konrad Zuse offered to build his Z2 computer to help the army, they couldn't see the need—and turned him down.
On the Allied side, great minds began to make great breakthroughs. In 1943, a team of mathematicians based at Bletchley Park near London, England (including Alan Turing) built a computer called Colossus to help them crack secret German codes. Colossus was the first fully
electronic computer. Instead of relays, it used a better form of switch known as a vacuum tube (also known, especially in Britain, as a valve). The vacuum tube, each one about as big as a person's thumb and glowing red hot like a tiny electric light bulb, had been invented in 1906 by
Lee de Forest(1873–1961), who named it the Audion. This breakthrough earned de Forest his nickname as "the father of radio" because their first major use was in
radio receivers, where they
amplified weak incoming signals so people could hear them more clearly. In computers such as the ABC and Colossus, vacuum tubes found an alternative use as faster and more compact switches.
Just like the codes it was trying to crack, Colossus was top-secret and its existence wasn't confirmed until after the war ended. As far as most people were concerned, vacuum tubes were pioneered by a more visible computer that appeared in 1946: the Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator (ENIAC). The ENIAC's inventors, two scientists from the University of Pennsylvania, John Mauchly (1907–1980) and J. Presper Eckert (1919–1995), were originally inspired by Bush's Differential Analyzer; years later Eckert recalled that ENIAC was the "descendant of Dr Bush's machine." But the machine they constructed was far more ambitious. It contained nearly 18,000 vacuum tubes (nine times more than Colossus), was around 24 m (80 ft) long, and weighed almost 30 tons. ENIAC is generally recognized as the world's first fully electronic, general-purpose, digital computer. Colossus might have qualified for this title too, but it was designed purely for one job (code-breaking); since it couldn't store a program, it couldn't easily be reprogrammed to do other things.
ENIAC was just the beginning. Its two inventors formed the Eckert Mauchly Computer Corporation in the late 1940s. Working with a brilliant Hungarian mathematician, John von Neumann (1903–1957), who was based at Princeton University, they then designed a better machine called EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer). In a key piece of work, von Neumann helped to define how the machine stored and processed its programs, laying the foundations for how all modern computers operate. After EDVAC, Eckert and Mauchly developed UNIVAC 1 (UNIVersal Automatic Computer) in 1951. They were helped in this task by a young, largely unknown American mathematician and Naval reserve named Grace Murray Hopper (1906–1992), who had originally been employed by Howard Aiken on the Harvard Mark I. Like Herman Hollerith's tabulator over 50 years before, UNIVAC 1 was used for processing data from the US census. It was then manufactured for other users—and became the world's first large-scale commercial computer.
Machines like Colossus, the ENIAC, and the Harvard Mark I compete for significance and recognition in the minds of computer historians. Which one was truly the first great modern computer? All of them and none: these—and several other important machines—evolved our idea of the modern electronic computer during the key period between the late 1930s and the early 1950s. Among those other machines were pioneering computers put together by English academics, notably the Manchester/Ferranti Mark I, built at Manchester University by Frederic Williams(1911–1977) and Thomas Kilburn (1921–2001), and the EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator), built byMaurice Wilkes (1913–2010) at Cambridge University.
The microelectronic revolution
Vacuum tubes were a considerable advance on relay switches, but machines like the ENIAC were notoriously unreliable. The modern term for a problem that holds up a computer program is a "bug." Popular legend has it that this word entered the vocabulary of computer programmers sometime in the 1950s when moths, attracted by the glowing lights of vacuum tubes, flew inside machines like the ENIAC, caused a short circuit, and brought work to a juddering halt. But there were other problems with vacuum tubes too. They consumed enormous amounts of power: the ENIAC used about 2000 times as much electricity as a modern laptop. And they took up huge amounts of space. Military needs were driving the development of machines like the ENIAC, but the sheer size of vacuum tubes had now become a real problem. ABC had used 300 vacuum tubes, Colossus had 2000, and the ENIAC had 18,000. The ENIAC's designers had boasted that its calculating speed was "at least 500 times as great as that of any other existing computing machine." But developing computers that were an order of magnitude more powerful still would have needed hundreds of thousands or even millions of vacuum tubes—which would have been far too costly, unwieldy, and unreliable. So a new technology was urgently required.

Photo: A typical transistor on an electronic circuit board.
The solution appeared in 1947 thanks to three physicists working at Bell Telephone Laboratories (Bell Labs).
John Bardeen(1908–1991),
Walter Brattain (1902–1987), and
William Shockley (1910–1989) were then helping Bell to develop new technology for the American public telephone system, so the electrical signals that carried phone calls could be amplified more easily and carried further. Shockley, who was leading the team, believed he could use semiconductors (materials such as germanium and silicon that allow electricity to flow through them only when they've been treated in special ways) to make a better form of
amplifier than the vacuum tube. When his early experiments failed, he set Bardeen and Brattain to work on the task for him. Eventually, in December 1947, they created a new form of amplifier that became known as the point-contact transistor. Bell Labs credited Bardeen and Brattain with the transistor and awarded them a patent. This enraged Shockley and prompted him to invent an even better design, the junction transistor, which has formed the basis of most
transistors ever since.
Like vacuum tubes, transistors could be used as amplifiers or as switches. But they had several major advantages. They were a fraction the size of vacuum tubes (typically about as big as a pea), used no power at all unless they were in operation, and were virtually 100 percent reliable. The transistor was one of the most important breakthroughs in the history of computing and it earned its inventors the world's greatest science prize, the
1956 Nobel Prize in Physics. By that time, however, the three men had already gone their separate ways. John Bardeen had begun pioneering research into
superconductivity, which would earn him a second Nobel Prize in 1972. Walter Brattain moved to another part of Bell Labs.
William Shockley decided to stick with the transistor, eventually forming his own corporation to develop it further. His decision would have extraordinary consequences for the computer industry. With a small amount of capital, Shockley set about hiring the best brains he could find in American universities, including young electrical engineer Robert Noyce (1927–1990) and research chemist Gordon Moore (1929–). It wasn't long before Shockley's idiosyncratic and bullying management style upset his workers. In 1956, eight of them—including Noyce and Moore—left Shockley Transistor to found a company of their own, Fairchild Semiconductor, just down the road. Thus began the growth of "Silicon Valley," the part of California centered on Palo Alto, where many of the world's leading computer and electronics companies have been based ever since.
It was in Fairchild's California building that the next breakthrough occurred—although, somewhat curiously, it also happened at exactly the same time in the Dallas laboratories of Texas Instruments. In Dallas, a young engineer from Kansas named
Jack Kilby (1923–2005) was considering how to improve the transistor. Although transistors were a great advance on vacuum tubes, one key problem remained. Machines that used thousands of transistors still had to be hand wired to connect all these components together. That process was laborious, costly, and error prone. Wouldn't it be better, Kilby reflected, if many transistors could be made in a single package? This prompted him to invent the "monolithic"
integrated circuit (IC), a collection of transistors and other components that could be manufactured all at once, in a block, on the surface of a semiconductor. Kilby's invention was another step forward, but it also had a drawback: the components in his integrated circuit still had to be connected by hand. While Kilby was making his breakthrough in Dallas, unknown to him, Robert Noyce was perfecting almost exactly the same idea at Fairchild in California. Noyce went one better, however: he found a way to include the connections between components in an integrated circuit, thus automating the entire process.
Integrated circuits, as much as transistors, helped to shrink computers during the 1960s. In 1943, IBM boss Thomas Watson had reputedly quipped: "I think there is a world market for about five computers." Just two decades later, the company and its competitors had installed around 25,000 large computer systems across the United States. As the 1960s wore on, integrated circuits became increasingly sophisticated and compact. Soon, engineers were speaking of large-scale integration (LSI), in which hundreds of components could be crammed onto a single chip, and then very large-scale integrated (VLSI), when the same chip could contain thousands of components.
The logical conclusion of all this miniaturization was that, someday, someone would be able to squeeze an entire computer onto a chip. In 1968, Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore had left Fairchild to establish a new company of their own. With integration very much in their minds, they called it Integrated Electronics or Intel for short. Originally they had planned to make memory chips, but when the company landed an order to make chips for a range of pocket calculators, history headed in a different direction. A couple of their engineers,Federico Faggin (1941–) and Marcian Edward (Ted) Hoff (1937–), realized that instead of making a range of specialist chips for a range of calculators, they could make a universal chip that could be programmed to work in them all. Thus was born the general-purpose, single chip computer or microprocessor—and that brought about the next phase of the computer revolution.
Personal computers
By 1974, Intel had launched a popular microprocessor known as the 8080 and computer hobbyists were soon building home computers around it. The first was the MITS Altair 8800, built by
Ed Roberts. With its front panel covered in red
LED lights and toggle switches, it was a far cry from modern PCs and laptops. Even so, it sold by the thousand and earned Roberts a fortune. The Altair inspired a Californian electronics wizard name
Steve Wozniak (1950–) to develop a computer of his own. "Woz" is often described as the hacker's "hacker"—a technically brilliant and highly creative engineer who pushed the boundaries of computing largely for his own amusement. In the mid-1970s, he was working at the Hewlett-Packard computer company in California, and spending his free time tinkering away as a member of the Homebrew Computer Club in the Bay Area.
After seeing the Altair, Woz used a 6502 microprocessor (made by an Intel rival, Mos Technology) to build a better home computer of his own: the Apple I. When he showed off his machine to his colleagues at the club, they all wanted one too. One of his friends,
Steve Jobs (1955–2011), persuaded Woz that they should go into business making the machine. Woz agreed so, famously, they set up Apple Computer Corporation in a garage belonging to Jobs' parents. After selling 175 of the Apple I for the devilish price of $666.66, Woz built a much better machine called the Apple ][ (pronounced "Apple Two"). While the Altair 8800 looked like something out of a science lab, and the Apple I was little more than a bare circuit board, the Apple ][ took its inspiration from such things as Sony televisions and stereos: it had a neat and friendly looking cream plastic case. Launched in April 1977, it was the world's first easy-to-use home "microcomputer." Soon home users, schools, and small businesses were buying the machine in their tens of thousands—at $1298 a time. Two things turned the Apple ][ into a really credible machine for small firms: a
disk drive unit, launched in 1978, which made it easy to store data; and a spreadsheet program called VisiCalc, which gave Apple users the ability to analyze that data. In just two and a half years, Apple sold around 50,000 of the machine, quickly accelerating out of Jobs' garage to become one of the world's biggest companies. Dozens of other microcomputers were launched around this time, including the TRS-80 from Radio Shack (Tandy in the UK) and the Commodore PET.
![Apple ][ microcomputer in a museum glass case](https://cdn4.explainthatstuff.com/appleII.jpg)

Photos: Microcomputers—the first PCs. The Apple ][ and The Sinclair ZX81, a build-it-yourself microcomputer that became hugely popular in the UK when it was launched in 1981. Both of these machines live in glass cases at Think Tank, the science museum in Birmingham, England.
Apple's success selling to businesses came as a great shock to IBM and the other big companies that dominated the computer industry. It didn't take a VisiCalc spreadsheet to figure out that, if the trend continued, upstarts like Apple would undermine IBM's immensely lucrative business market selling "Big Blue" computers. In 1980, IBM finally realized it had to do something and launched a highly streamlined project to save its business. One year later, it released the IBM Personal Computer (PC), based on an Intel 8080 microprocessor, which rapidly reversed the company's fortunes and stole the market back from Apple.
The PC was successful essentially for one reason. All the dozens of microcomputers that had been launched in the 1970s—including the Apple ][—were incompatible. All used different hardware and worked in different ways. Most were programmed using a simple, English-like language called BASIC, but each one used its own flavor of BASIC, which was tied closely to the machine's hardware design. As a result, programs written for one machine would generally not run on another one without a great deal of conversion. Companies who wrote software professionally typically wrote it just for one machine and, consequently, there was no software industry to speak of.
In 1976, Gary Kildall (1942–1994), a teacher and computer scientist, and one of the founders of the Homebrew Computer Club, had figured out a solution to this problem. Kildall wrote an operating system (a computer's fundamental control software) called CP/M that acted as an intermediary between the user's programs and the machine's hardware. With a stroke of genius, Kildall realized that all he had to do was rewrite CP/M so it worked on each different machine. Then all those machines could run identical user programs—without any modification at all—inside CP/M. That would make all the different microcomputers compatible at a stroke. By the early 1980s, Kildall had become a multimillionaire through the success of his invention: the first personal computer operating system. Naturally, when IBM was developing its personal computer, it approached him hoping to put CP/M on its own machine. Legend has it that Kildall was out flying his personal plane when IBM called, so missed out on one of the world's greatest deals. But the truth seems to have been that IBM wanted to buy CP/M outright for just $200,000, while Kildall recognized his product was worth millions more and refused to sell. Instead, IBM turned to a young programmer named Bill Gates (1955–). His then tiny company, Microsoft, rapidly put together an operating system called DOS, based on a product called QDOS (Quick and Dirty Operating System), which they acquired from Seattle Computer Products. Some believe Microsoft and IBM cheated Kildall out of his place in computer history; Kildall himself accused them of copying his ideas. Others think Gates was simply the shrewder businessman. Either way, the IBM PC, powered by Microsoft's operating system, was a runaway success.
Yet IBM's victory was short-lived. Cannily, Bill Gates had sold IBM the rights to one flavor of DOS (PC-DOS) and retained the rights to a very similar version (MS-DOS) for his own use. When other computer manufacturers, notably Compaq and Dell, starting making IBM-compatible (or "cloned") hardware, they too came to Gates for the software. IBM charged a premium for machines that carried its badge, but consumers soon realized that PCs were commodities: they contained almost identical components—an Intel microprocessor, for example—no matter whose name they had on the case. As IBM lost market share, the ultimate victors were Microsoft and Intel, who were soon supplying the software and hardware for almost every PC on the planet. Apple, IBM, and Kildall made a great deal of money—but all failed to capitalize decisively on their early success.

Photo: Personal computers threatened companies making large "mainframes" like this one. Picture courtesy of NASA on the Commons (where you can download a larger version).
The user revolution
Fortunately for Apple, it had another great idea. One of the Apple II's strongest suits was its sheer "user-friendliness." For Steve Jobs, developing truly easy-to-use computers became a personal mission in the early 1980s. What truly inspired him was a visit to PARC (Palo Alto Research Center), a cutting-edge computer laboratory then run as a division of the Xerox Corporation. Xerox had started developing computers in the early 1970s, believing they would make
paper (and the highly lucrative
photocopiers Xerox made) obsolete. One of PARC's research projects was an advanced $40,000 computer called the Xerox Alto. Unlike most microcomputers launched in the 1970s, which were programmed by typing in text commands, the Alto had a desktop-like screen with little picture icons that could be moved around with a mouse: it was the very first graphical user interface (GUI, pronounced "gooey")—an idea conceived by
Alan Kay (1940–) and now used in virtually every modern computer. The Alto borrowed some of its ideas, including the
mouse, from 1960s computer pioneer
Douglas Engelbart (1925–2013).
Back at Apple, Jobs launched his own version of the Alto project to develop an easy-to-use computer called PITS (Person In The Street). This machine became the Apple Lisa, launched in January 1983—the first widely available computer with a GUI desktop. With a retail price of $10,000, over three times the cost of an IBM PC, the Lisa was a commercial flop. But it paved the way for a better, cheaper machine called the Macintosh that Jobs unveiled a year later, in January 1984. With its memorable launch ad for the Macintosh inspired by George Orwell's novel 1984, and directed by Ridley Scott (director of the dystopic movie Blade Runner), Apple took a swipe at IBM's monopoly, criticizing what it portrayed as the firm's domineering—even totalitarian—approach: Big Blue was really Big Brother. Apple's ad promised a very different vision: "On January 24, Apple Computer will introduce Macintosh. And you'll see why 1984 won't be like '1984'." The Macintosh was a critical success and helped to invent the new field of desktop publishing in the mid-1980s, yet it never came close to challenging IBM's position.
Ironically, Jobs' easy-to-use machine also helped Microsoft to dislodge IBM as the world's leading force in computing. When Bill Gates saw how the Macintosh worked, with its easy-to-use picture-icon desktop, he launched Windows, an upgraded version of his MS-DOS software. Apple saw this as blatant plagiarism and filed a $5.5 billion copyright lawsuit in 1988. Four years later, the case collapsed with Microsoft effectively securing the right to use the Macintosh "look and feel" in all present and future versions of Windows. Microsoft's Windows 95 system, launched three years later, had an easy-to-use, Macintosh-like desktop and MS-DOS running behind the scenes.
Photo: The IBM Blue Gene/P supercomputer at Argonne National Laboratory: one of the world's most powerful computers. Picture courtesy of Argonne National Laboratory published on Flickr in 2009 under a Creative Commons Licence.
From nets to the Internet
Standardized PCs running standardized software brought a big benefit for businesses: computers could be linked together into
networks to share information. At Xerox PARC in 1973, electrical engineer
Bob Metcalfe(1946–) developed a new way of linking computers "through the ether" (empty space) that he called Ethernet. A few years later, Metcalfe left Xerox to form his own company, 3Com, to help companies realize "Metcalfe's Law": computers become useful the more closely connected they are to other people's computers. As more and more companies explored the power of local area networks (LANs), so, as the 1980s progressed, it became clear that there were great benefits to be gained by connecting computers over even greater distances—into so-called wide area networks (WANs).

Photo: Computers aren't what they used to be: they're much less noticeable because they're much more seamlessly integrated into everyday life. Some are "embedded" into household gadgets like coffee makers or televisions. Others travel round in our pockets in our smartphones—essentially pocket computers that we can program simply by downloading "apps" (applications).
Today, the best known WAN is the
Internet—a global network of individual computers and LANs that links up hundreds of millions of people. The history of the Internet is another story, but it began in the 1960s when four American universities launched a project to connect their computer systems together to make the first WAN. Later, with funding for the Department of Defense, that network became a bigger project called ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network). In the mid-1980s, the US National Science Foundation (NSF) launched its own WAN called NSFNET. The convergence of all these networks produced what we now call the Internet later in the 1980s. Shortly afterward, the power of networking gave British computer programmer
Tim Berners-Lee(1955–) his big idea: to combine the power of computer networks with the information-sharing idea Vannevar Bush had proposed in 1945. Thus, was born the
World Wide Web—an easy way of sharing information over a computer network, which made possible the modern age of
cloud computing (where anyone can access vast computing power over the Internet without having to worry about where or how their data is processed). It's Tim Berners-Lee's invention that brings you this potted history of computing today!









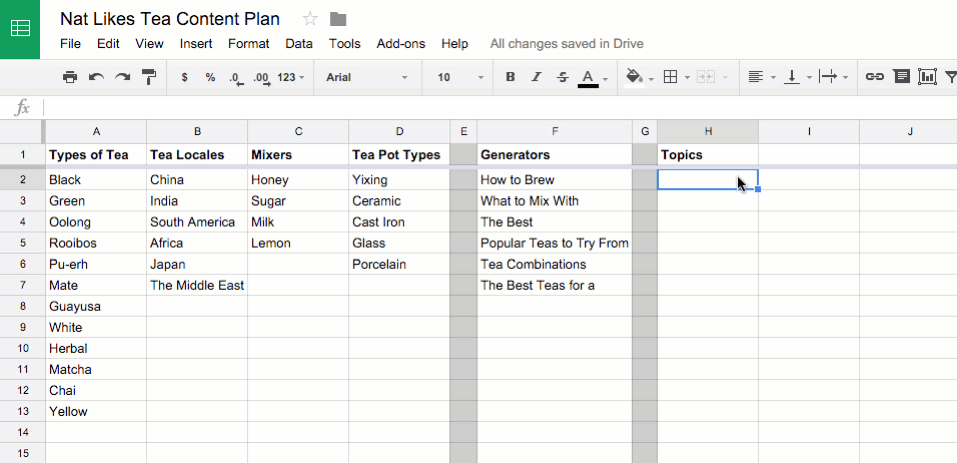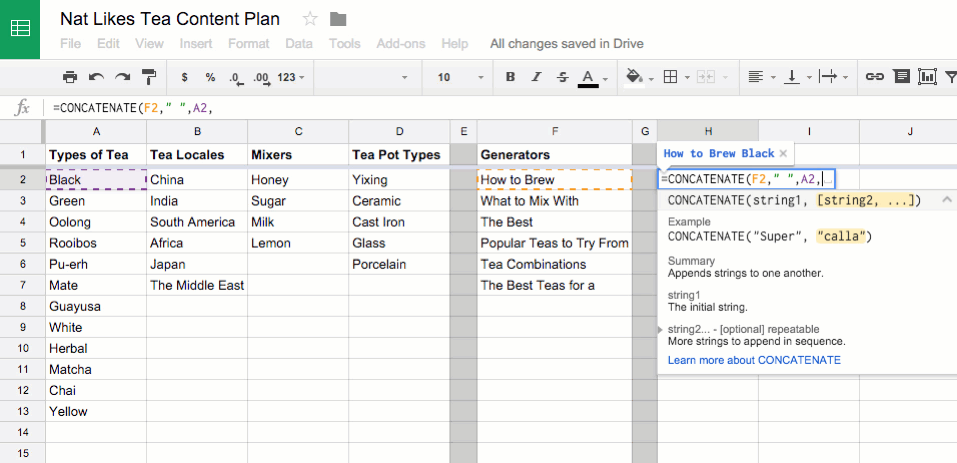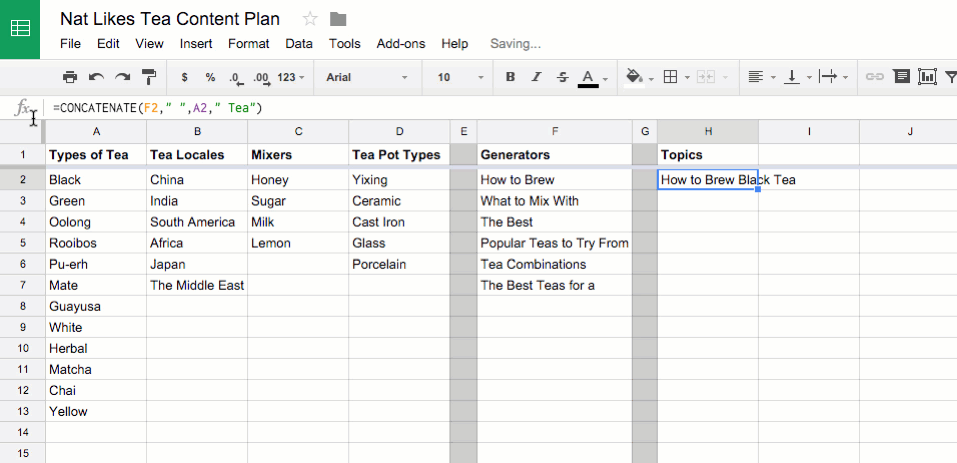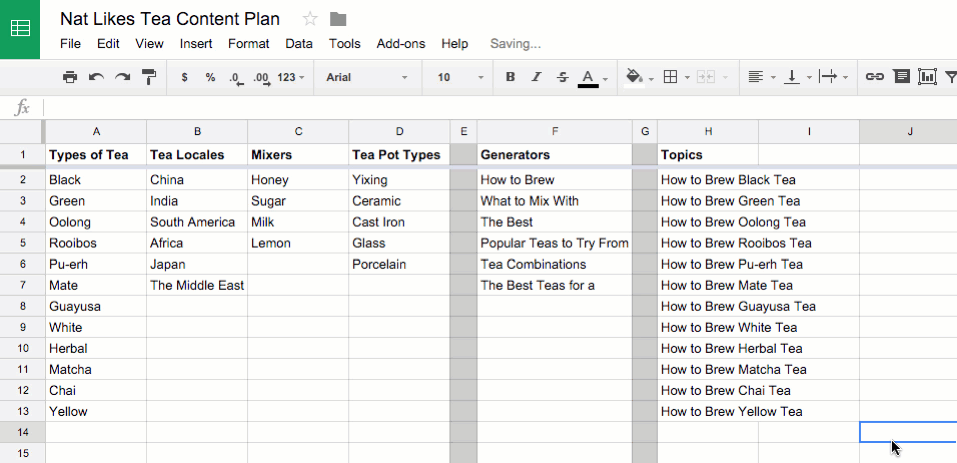
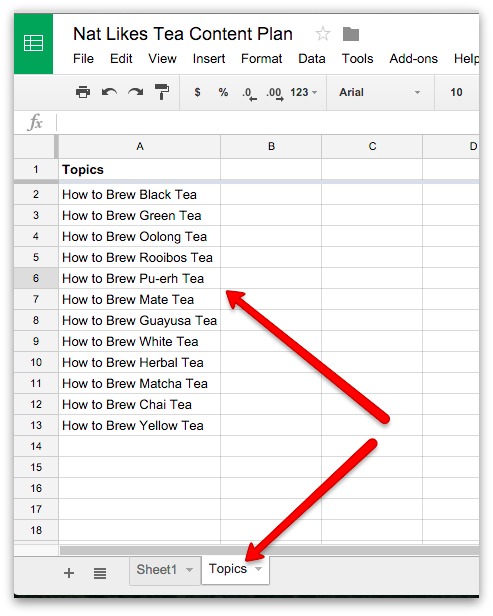
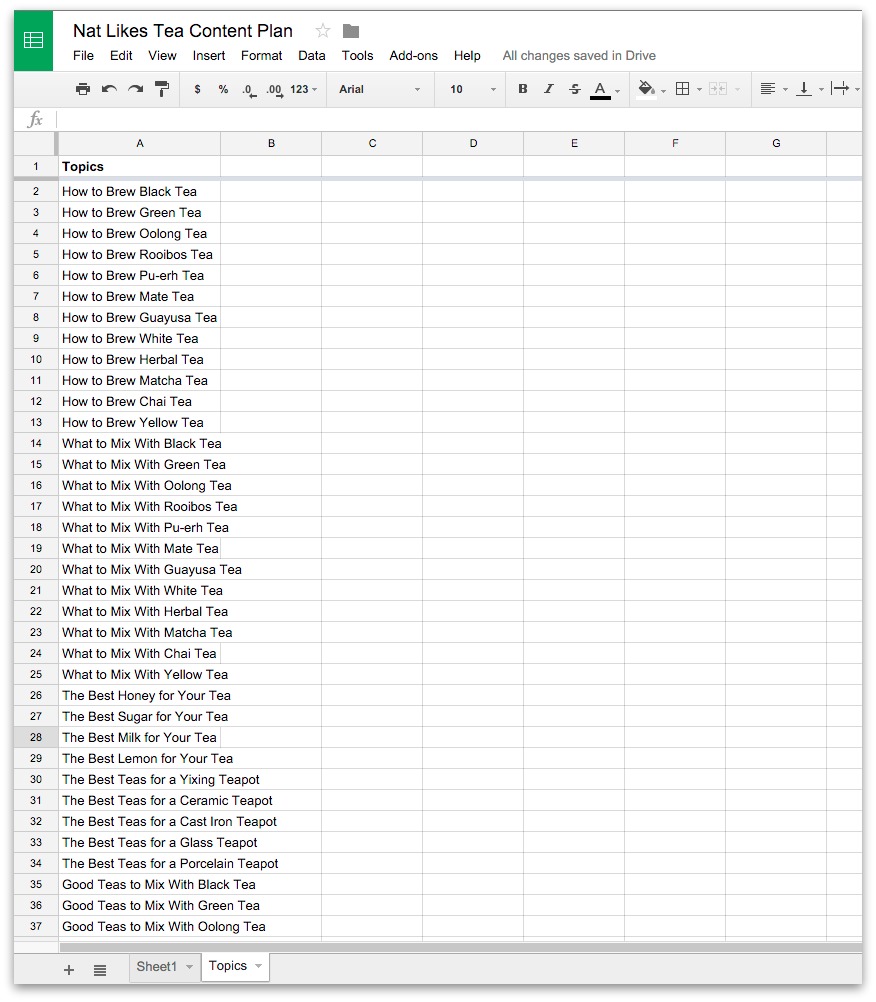








![Apple ][ microcomputer in a museum glass case](https://cdn4.explainthatstuff.com/appleII.jpg)




